Graphical model
A graphical model is a probabilistic model for which a graph denotes the conditional independence structure between random variables. They are commonly used in probability theory, statistics—particularly Bayesian statistics—and machine learning.
Contents |
Types of graphical models
Generally, probabilistic graphical models use a graph-based representation as the foundation for encoding a complete distribution over a multi-dimensional space and a graph that is a compact or factorized representation of a set of independences that hold in the specific distribution. Two branches of graphical representations of distributions are commonly used, namely, Bayesian networks and Markov networks. Both families encompass the properties of factorization and independences, but they differ in the set of independences they can encode and the factorization of the distribution that they induce.[1]
Bayesian network
If the network structure of the model is a directed acyclic graph, the model represents a factorization of the joint probability of all random variables. More precisely, if the events are  then the joint probability satisfies
then the joint probability satisfies
where  is the set of parents of node
is the set of parents of node 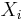 . In other words, the joint distribution factors into a product of conditional distributions. Any two nodes are conditionally independent given the values of their parents. In general, any two sets of nodes are conditionally independent given a third set if a criterion called d-separation holds in the graph. Local independences and global independences are equivalent in Bayesian networks.
. In other words, the joint distribution factors into a product of conditional distributions. Any two nodes are conditionally independent given the values of their parents. In general, any two sets of nodes are conditionally independent given a third set if a criterion called d-separation holds in the graph. Local independences and global independences are equivalent in Bayesian networks.
This type of graphical model is known as a directed graphical model, Bayesian network, or belief network. Classic machine learning models like hidden Markov models, neural networks and newer models such as variable-order Markov models can be considered special cases of Bayesian networks.
Markov random field
A Markov random field, also known as a Markov network, is a model over an undirected graph. A graphical model with many repeated subunits can be represented with plate notation.
Other types
- A factor graph is an undirected bipartite graph connecting variables and factors. Each factor represents a probability distribution over the variables it is connected to. Graphs are converted into factor graph form to perform belief propagation.
- A clique tree or junction tree is a tree of cliques, used in the junction tree algorithm.
- A chain graph is a graph which may have both directed and undirected edges, but without any directed cycles (i.e. if we start at any vertex and move along the graph respecting the directions of any arrows, we cannot return to the vertex we started from if we have passed an arrow). Both directed acyclic graphs and undirected graphs are special cases of chain graphs, which can therefore provide a way of unifying and generalizing Bayesian and Markov networks.[2]
- An ancestral graph is a further extension, having directed, bidirected and undirected edges.[3]
- A conditional random field is a discriminative model specified over an undirected graph.
- A restricted Boltzmann machine is a generative model specified over an undirected graph.
Applications
The framework of the models, which provides algorithms for discovering and analyzing structure in complex distributions to describe them succinctly and extract the unstructured information, allows them to be constructed and utilized effectively.[1] Applications of graphical models include information extraction, speech recognition, computer vision, decoding of low-density parity-check codes, modeling of gene regulatory networks, gene finding and diagnosis of diseases, and graphical models for protein structure.
See also
Notes
- ^ a b Koller; Friedman (2009). Probabilistic Graphical Models. Massachusetts: MIT Press. ISBN 0-262-01319-3.
- ^ Frydenberg, Morten (1990). "The Chain Graph Markov Property". Scandinavian Journal of Statistics 17 (4): 333–353. JSTOR 4616181. MR1096723.
- ^ Richardson, Thomas; Spirtes, Peter (2002). "Ancestral graph Markov models". Annals of Statistics 30 (4): 962–1030. doi:10.1214/aos/1031689015. MR1926166. Zbl 1033.60008.
References and further reading
Books and book chapters
- Bishop, Christopher M. (2006). "Chapter 8. Graphical Models". Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Springer. pp. 359–422. ISBN 0-387-31073-8. MR2247587. http://research.microsoft.com/~cmbishop/PRML/Bishop-PRML-sample.pdf.
- Cowell, Robert G.; Dawid, A. Philip; Lauritzen, Steffen L.; Spiegelhalter, David J. (1999). Probabilistic networks and expert systems. Berlin: Springer. ISBN 0-387-98767-3. MR1697175. A more advanced and statistically oriented book
- Jensen, Finn (1996). An introduction to Bayesian networks. Berlin: Springer. ISBN 0-387-91502-8.
- Koller, D.; Friedman, N. (2009). Probabilistic Graphical Models. Massachusetts: MIT Press. pp. 1208. ISBN 0-262-01319-3.
- Pearl, Judea (1988). Probabilistic Reasoning in Intelligent Systems (2nd revised ed.). San Mateo, CA: Morgan Kaufmann. ISBN 1558604790. MR0965765. A computational reasoning approach, where the relationships between graphs and probabilities were formally introduced.
Journal articles
- Edoardo M. Airoldi (2007). "Getting Started in Probabilistic Graphical Models". PLoS Computational Biology 3 (12): e252. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030252. PMC 2134967. PMID 18069887. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2134967.
- Jordan, M. I. (2004). "Graphical Models". Statistical Science 19: 140–155. doi:10.1214/088342304000000026.
![P[X_1,\ldots,X_n]=\prod_{i=1}^nP[X_i|pa_i]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/cdee2242c1e84db8c1cc05ee3f95fec7.png)